For watching the video version of this article, click on the video below.
What is the cause of chronic, low-grade, and systemic inflammation?
What is the connection between inflammation and aging?
What is the connection between inflammation and chronic diseases?
What is the cause of chronic, low-grade, and systemic inflammation?
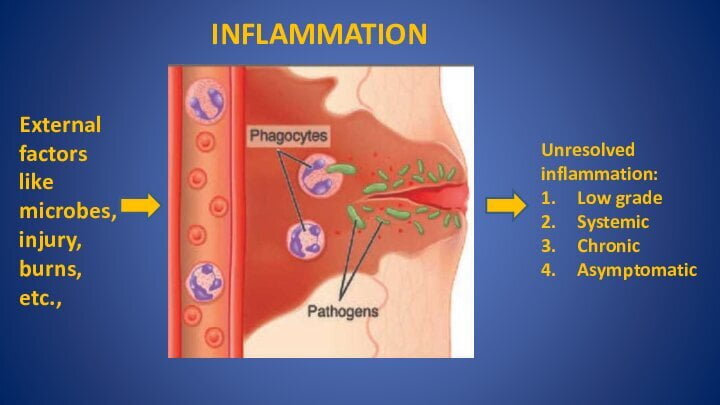
Inflammation is the response of the body to a number of external unfavorable factors. Examples of these factors include infectious microbes, injury, burns, etc. A number of cells including phagocytes like leukocytes and macrophages reach the site of entry of the microbe or injury. These cells secrete various chemicals like interleukins, etc., and try to clear the triggering agent. When the agent is cleared, cells and mediators secreted by these cells bring about the resolution of the inflammatory process.
Inflammation is a delicate balance between substances that drive it, and later on, substances that halt it. In some cases, the body is unable to clear the agent completely. In these cases, low levels of the agent, and inflammatory cells and chemicals continue to persist at the site for long periods. This is known as an ‘unresolved inflammation’. This local inflammation present in one organ, can spill over to multiple organs, and become what is known as a ‘systemic inflammation’ involving the entire body. This chronic, systemic, and low-grade inflammation is asymptomatic, and the person having it is unaware of it going on inside his body.
What is the connection between inflammation and aging?
Inflammation is usually beneficial as it helps to protect the body against a number of external factors. However, it can become the reason for harm to the body when it is unresolved and persistent for long periods. It is present in a number of chronic diseases. It is also a common feature in the process of aging.
It is observed that older people have higher baseline levels of inflammation. This is called ‘inflammaging’. Inflammaging, in part, is due to immunosenescence (i.e. aging of the immune system). That is to say, that as people get older, their immune system also becomes old and less efficient in clearing foreign agents like antigens. This causes prolonged lingering of foreign agents in the body, causing chronic low-grade inflammation.
What is the connection between inflammation and chronic diseases?
Inflammation is associated with many age-related chronic diseases. Some of the most common ones are discussed here. It is seen in atherosclerosis (Boren et al., 2004). Atherosclerosis is a condition in which there is formation of plaques in the arteries supplying blood to organs like the heart and brain. These plaques can complicate suddenly, resulting in heart attacks and brain strokes. It is also seen in hypertension (Miguel et al., 2015). It is present in type-2 diabetes mellitus (Franceschi et al., 2001). Diabetes mellitus is a condition in which glucose levels are chronically high in the blood. Persistent high levels of glucose eventually cause damage to organs like the eyes, kidneys, and blood vessels. It is associated with conditions like Alzheimer’s disease (which is responsible for the decline in memory and functioning with age) (Giunta et al., 2008), osteoporosis (which is the leading cause of fractures in the elderly) (Lencel et al., 2011), respiratory infections (Meyer et al., 2010), and many types of cancers (Singh et al., 2019). It is seen in frailty (Leng et al., 2007). Frailty is a condition in the elderly characterized by weight loss, weakness, reduced physical activity, reduced grip strength, slowness, and most importantly, inability to cope with acute stressors like infections, trauma, etc. Frailty is due to physiological aging in various organ systems. Frailty is responsible for unfavorable outcomes in the elderly like frequent complications after interventions, hospitalizations, etc. Finally, it is present in obesity (Lee et al., 2013). However, it is still unclear whether inflammation is responsible for causing these diseases, or there is merely an association of inflammation with these conditions.
Chronic low-grade systemic inflammation can also be caused by exposure to air pollutants. To read about the harmful effects of air pollution on health, click here.
Inflammation can be reduced in a natural way by following an anti-inflammatory diet.
If you found the information in this article useful and would like to receive updates on health-related articles in the future, consider subscribing by providing your e-mail.
References:
- Shijin Xia, et al., An Update on Inflamm-Aging: Mechanisms, Prevention, and Treatment. 2017.
- Anne M. Minihane et al., Low-grade inflammation, diet composition and health: current research evidence and its translation. 2015.
- Andrea Ticinesi et al., Nutrition and Inflammation in Older Individuals: Focus on Vitamin D, n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Whey Proteins. 2016.
- Philip C. Calder et al., Health relevance of the modification of low grade inflammation in ageing (inflammageing) and the role of nutrition. 2017.
- Custodero et al., Evidence-based nutritional and pharmacological interventions targeting chronic low-grade inflammation in middle-age and older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. 2018.
Disclaimer:
The information on this website is strictly for educational purposes only. This information is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, and treatment. Always consult a qualified medical professional for any advice regarding a medical condition. Do not disregard any professional medical advice or delay in seeking medical help because of any content on this website. Although every effort is made to provide the latest, accurate, and comprehensive information in this content, the author does not take any liability for any damage arising from any use of this content. The content is provided as-is and without any warranties.
